Networks are like the roads of the internet, helping data travel from one point to another. Just as traffic lights and signs keep cars from crashing into each other on roads, networks use special rules to prevent data from colliding and causing data jams. One key set of rules is called the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), and it's crucial for keeping networks smooth and crash-free.
In the world of Cisco networks, there are two advanced versions of STP that we're focusing on: Per-VLAN Spanning Tree (PVST) and Rapid Per-VLAN Spanning Tree (Rapid PVST).
These versions are like the superheroes of network traffic control, each with its own set of powers to keep data moving efficiently and safely.
PVST allows different parts of a network to talk to each other without getting tangled up, making it possible for large networks to be well-organized and reliable. On the other hand, Rapid PVST is like PVST but supercharged, making everything happen faster and more smoothly, ensuring that if something goes wrong, the network can recover quickly, keeping data flowing without interruption.
This blog will guide you step by step on how to configure both PVST and Rapid PVST on Cisco devices. By following these instructions, you'll be able to enhance your network's performance, making it more reliable and efficient. Whether you're a network engineer or someone keen to understand how to optimize network traffic, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to make the most of Cisco's powerful networking capabilities.
Understanding Spanning Tree Protocols
Imagine networks as complex road systems. Without proper rules and guidance, cars (or in our case, data packets) could easily get lost, crash, or end up going in circles, causing what's known as traffic congestion. This is where Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) comes into play. It acts as the traffic controller of the network, ensuring data packets find the most efficient route to their destination without causing any loops or congestion.
STP and its Role in Network Stability
At its core, STP is about preventing these data traffic jams. It does this by blocking potential loop paths within the network, effectively ensuring that data takes only the safest and most direct routes. You can think of STP as a traffic officer at a busy intersection, directing the flow of cars to keep everything running smoothly and safely.
Per-VLAN Spanning Tree (PVST)
Per-VLAN Spanning Tree (PVST) takes this a step further by applying these traffic rules to each VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) individually. This means that each VLAN has its own unique set of traffic paths, tailored to prevent loops and ensure data packets within that VLAN are routed efficiently. PVST's approach is akin to having personalized traffic plans for different neighborhoods within a city, each optimized to prevent congestion and ensure a smooth flow of vehicles.
PVST not only enhances network flexibility and efficiency, especially in complex or large-scale network environments, but it also allows for more granified control over the routing of data packets. This can lead to significant improvements in overall network performance and reliability.
By understanding the roles of STP and PVST in maintaining network stability and efficiency, network administrators can better design, implement, and manage their network infrastructures, ensuring optimal performance and minimal disruptions.
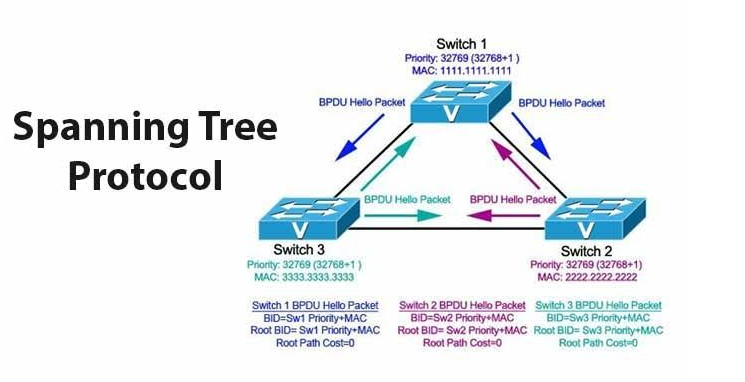
Configuring PVST on Cisco Devices
After understanding the role and benefits of PVST in enhancing network performance and stability, it's time to dive into how you can configure Per-VLAN Spanning Tree on your Cisco devices. This process is like setting up the rules for how traffic should flow across the network, ensuring each VLAN has its own dedicated path, minimizing the risk of traffic jams and data collisions.
Pre-requisites for PVST Configuration
Before jumping into the configuration steps, it's essential to ensure your network and devices meet the following conditions:
- Ensure all devices are Cisco: PVST is a Cisco proprietary protocol, so it works best within a Cisco ecosystem.
- Update to the latest firmware: Having the latest software on your devices can prevent compatibility issues.
- Plan your VLANs: Know how your network is segmented into VLANs, as PVST will be applied to these segments.
Step-by-Step Configuration Guide
- Access the Switch
- Start by logging into your Cisco switch via a console or SSH connection. You'll need administrative access to make these changes.
- Enter Global Configuration Mode
- Once logged in, enter the global configuration mode by typing configure terminal or conf t for short.
- Enable Spanning Tree PVST
- For each VLAN that you want to apply PVST to, you'll need to specify it by using the command spanning-tree vlan [VLAN_ID] priority [PRIORITY_VALUE]. The VLAN ID is the identifier for your VLAN, and the priority value determines the switch's role in the spanning tree for that VLAN. A lower number gives the switch a better chance of being elected as the root bridge.
- Adjust Spanning Tree Parameters (Optional)
- You might want to tweak some settings to optimize performance, such as the hello time, max age, and forward delay. Use the spanning-tree vlan [VLAN_ID] [setting] [value] command to make these adjustments.
- Verify Your Configuration
- After configuring PVST, it's crucial to verify that everything is set up correctly. Use the show spanning-tree command to view the spanning tree status for your VLANs. This command helps ensure that the spanning tree is operational and that the settings are applied as expected.
- Save Your Configuration
- Don't forget to save your configuration with the write memory or copy running-config startup-config command. This action ensures that your settings persist after a reboot.
By carefully following these steps, you've successfully configured PVST on your Cisco devices, optimizing your network for better performance, stability, and efficiency.
This process not only enhances the reliability of your network but also ensures that each VLAN operates with its own best path for data traffic, reducing the chances of network loops and congestion.
Best Practices for Spanning Tree Configuration
Configuring the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP), including PVST and Rapid PVST, on Cisco devices is a pivotal task to ensure network stability and efficiency. Beyond the initial configuration, adhering to best practices is crucial for maximizing your network's performance and reliability. These guidelines will help maintain a robust and agile network.
Optimize Spanning Tree Performance
- Strategically Place the Root Bridge: The root bridge's location within the network is vital. Placing it centrally minimizes topology changes and optimizes data paths, significantly enhancing network efficiency. For an in-depth understanding, consider our Spanning Tree Protocol course, which covers root bridge selection and other optimization strategies.
- Prioritize Switches with Care: Lower priorities should be assigned to central or critical switches. This influences their role as root or backup root bridges, fostering network stability.
- Minimize STP Instances: Simplify your network by limiting STP instances. Effective VLAN management and network design can prevent unnecessary burdens on network resources.
- Activate PortFast on Edge Ports: Ports connecting directly to end devices, not switches, should have PortFast enabled. This setting allows them to bypass the usual STP listening and learning states, speeding up the network's response to changes.
- Implement BPDU Guard with PortFast: To safeguard against potential network loops, enable BPDU Guard on PortFast-configured ports. This precaution disables ports if they unexpectedly receive BPDU packets, indicating a potential loop scenario.
Monitoring and Troubleshooting
- Keep an Eye on Spanning Tree Status: Commands like show spanning-tree summary offer insights into the health and operation of your spanning tree. Regular monitoring helps identify and rectify issues proactively.
- Document Your Configuration: Detailed records of your STP setup, including root bridge placements and priorities, are invaluable for troubleshooting and ensuring consistent configurations.
- Develop a Recovery Plan: Being prepared with strategies for addressing STP-related network problems is essential. This includes methods for swift issue identification, isolation, and reversal of changes when necessary.
By following these best practices and incorporating Spanning Tree Protocol training into your learning path, you can significantly improve the performance and resilience of your network. STP, when correctly implemented and managed, forms a strong foundation for any network's infrastructure.
Summary
Configuring Per-VLAN Spanning Tree (PVST) and Rapid Per-VLAN Spanning Tree (Rapid PVST) on Cisco devices is more than just a technical necessity; it's a strategic move to ensure your network's optimal performance and reliability.
Through this blogpost, we've navigated the intricacies of STP, from understanding its foundational principles to implementing best practices that enhance network stability and efficiency.
Spanning Tree Protocol plays a pivotal role in preventing network loops and ensuring that data packets find the most efficient path through your network. By applying the configurations and practices outlined, you're not just preventing potential issues; you're proactively building a network that is resilient, responsive, and ready for the challenges of modern data traffic demands.
As you move forward, keep these practices in mind, and consider enhancing your knowledge with specialized courses. The journey to network excellence is ongoing, and every step you take towards understanding and implementing protocols like STP brings you closer to achieving a robust, efficient, and reliable network infrastructure.


