In the dynamic world of networking, the Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) stands out as a cornerstone of efficient multicast group management. Essential for the delivery of content from one-to-many or many-to-many models, IGMP orchestrates the communication necessary for streaming video, online gaming, and even the broad distribution of software updates across IPv4 networks.
As we peel back the layers of IGMP, we will explore the nuts and bolts of how IGMP queries, joins, and membership reports enable the selective transmission of data, ensuring that network resources are utilized optimally.
Understanding IGMP and its operational mechanisms is not just a technical necessity; it's a prerequisite for designing and maintaining networks that are both resilient and efficient. From the foundational IGMPv1 to the more sophisticated IGMPv3, each version introduces improvements that refine multicast group management, offering nuanced control over who receives what data and when.
As we delve into the specifics of IGMP queries, joins, and membership reports, keep in mind the pivotal role these elements play in the orchestration of multicast communication. By the end of this article, you'll not only understand IGMP's operational mechanics but also appreciate its significance in the broader context of network management and efficiency.
Understanding IGMP
The Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) serves as the backbone of multicast group management on IPv4 networks, facilitating a streamlined approach to content delivery across diverse applications. By enabling a host to inform its local router of its desire to participate in specific multicast groups, IGMP plays a critical role in the efficient distribution of data.
IGMP Overview
At its core, IGMP enhances the efficiency of network resources by ensuring that multicast traffic is directed only to the hosts that have explicitly requested it. This selective data transmission is crucial for applications requiring one-to-many communication, such as streaming media and online gaming.
For those keen on diving deeper into the technical aspects and real-world applications of IGMP, our Self-Paced Multicast Training course provides an extensive curriculum designed to enhance your understanding and skills in multicast networking.
- The Role of IGMP in Network Efficiency
By managing host memberships in multicast groups, IGMP significantly reduces unnecessary network traffic, conserving bandwidth, and optimizing the delivery of multicast content. This is particularly important in environments where network resources are at a premium, and efficiency is paramount.
IGMP Operations
- IGMP Queries
IGMP queries are fundamental to the protocol's operation, initiating the process of group membership determination. These queries can be general, targeting all hosts, or specific, aimed at members of a particular multicast group. The ability to distinguish between these types of queries allows for more granular control over multicast group memberships. - Joining a Multicast Group (IGMP Join)
The IGMP join process is initiated by hosts wishing to receive multicast traffic for a specific group. This process underscores the dynamic nature of multicast group memberships, allowing for real-time adjustments based on host requests. - IGMP Membership Reports
Membership reports are critical in affirming a host's intention to join or remain in a multicast group. These reports serve as a direct communication line between hosts and routers, ensuring that multicast traffic is efficiently routed to interested parties. - Leaving a Multicast Group
Equally important is the ability of hosts to leave multicast groups, signaling through IGMP that they no longer wish to receive specific multicast traffic. This mechanism supports the dynamic optimization of network resources, adapting to changing needs and interests of network participants.
The Significance of IGMP in Modern Networks
Understanding and leveraging IGMP is essential for network administrators and IT professionals who manage complex networking environments. Its role in ensuring the efficient use of network resources cannot be overstated, particularly as demand for multicast applications continues to grow.
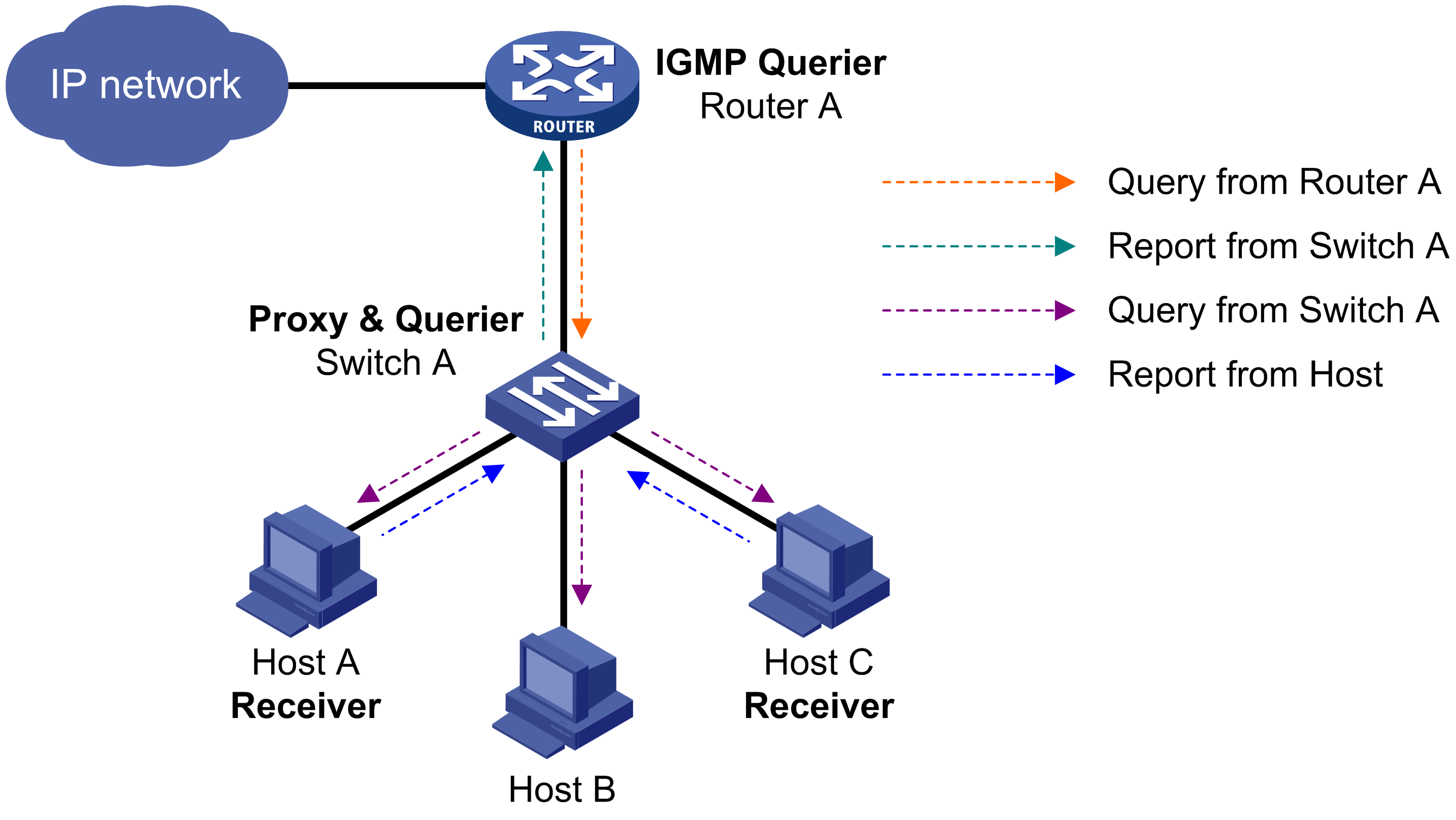
Practical Applications and Importance of IGMP
IGMP's design to manage multicast group memberships on IPv4 networks has far-reaching implications for network efficiency and data distribution. By ensuring that multicast traffic is only sent to hosts that have explicitly requested it, IGMP plays a crucial role in the optimization of network resources, particularly in environments where bandwidth conservation and targeted content delivery are key.
Real-World Applications of IGMP
- Internet Television and Streaming Media
The use of IGMP in internet television and streaming media services is perhaps the most recognizable application. By managing subscriber memberships to different multicast streams, IGMP allows for the efficient distribution of high-bandwidth content such as live video feeds and on-demand streaming, ensuring that only interested hosts receive the data. - Online Gaming
In online gaming, IGMP facilitates the creation of multicast groups for players in the same game instance, enabling the efficient broadcast of game state updates. This is critical for maintaining real-time synchronization between players and the game server, enhancing the overall gaming experience. - Virtual Meetings and Collaborative Work
Virtual meeting platforms and collaborative work tools utilize IGMP to efficiently distribute audio and video feeds to participants. In corporate environments where bandwidth efficiency is paramount, IGMP's role in reducing redundant data transmission is invaluable.
The Importance of IGMP in Network Efficiency
The selective nature of IGMP's multicast group management underpins its significance in modern networks. By minimizing unnecessary multicast traffic, IGMP contributes to:
- Reduced Network Congestion: By ensuring that only interested hosts receive multicast traffic, IGMP plays a vital role in preventing network congestion, particularly in densely populated network environments.
- Bandwidth Conservation: In an era where bandwidth is a precious resource, IGMP's efficiency in data distribution helps conserve bandwidth, which is especially critical for bandwidth-intensive applications like HD video streaming.
- Improved Application Performance: For applications that rely on timely data distribution to multiple recipients, IGMP's ability to streamline multicast traffic contributes to enhanced application performance and user satisfaction.
Challenges and Security Considerations
While IGMP significantly enhances network efficiency, it is not without its challenges and security considerations. Being proactive in addressing potential vulnerabilities and understanding the implications of IGMP configurations is essential for maintaining a secure and efficient network.
For networking professionals and enthusiasts eager to stay at the forefront of technology, continuous learning is essential. Our Self-Paced Multicast Training course represents just the beginning of your journey into multicast networking.
Summary
IGMP has proven itself as an indispensable protocol within the realm of IPv4 networking, especially for applications requiring efficient multicast communication. Its mechanisms for managing multicast group memberships ensure that data is delivered in the most efficient manner possible, conserving bandwidth and reducing unnecessary network traffic.
Key Takeaways
- Efficient Network Resource Utilization: IGMP's contribution to reducing network congestion and optimizing bandwidth usage cannot be overstated. Its selective data distribution model is crucial for networks supporting high-bandwidth applications like streaming services and online gaming.
- Adaptability and Scalability: The evolution from IGMPv1 to IGMPv3 showcases the protocol's adaptability to changing network demands, offering more granular control over multicast memberships and source-specific multicasting.
- Security and Challenges: While IGMP enhances network efficiency, it also requires diligent management to mitigate potential vulnerabilities. Understanding and addressing these concerns is key for maintaining network security and performance.
Looking Ahead
As we look towards the future, the transition to IPv6 and the increasing demand for multicast applications highlight the ongoing need for protocols like IGMP. The principles underlying IGMP will continue to inform the development of multicast management protocols, ensuring that networks remain capable of supporting the next generation of internet applications.


