In the world of networking, making sure your network is both efficient and robust is key. Two technologies stand out when it comes to optimizing network performance: Port Channel and EtherChannel.
At first glance, they might seem similar, as both aim to aggregate multiple network links into a single logical one. This not only boosts the available bandwidth but also provides redundancy, ensuring that network communication remains uninterrupted even if one link fails.
This blogpost dives deep into Port Channel and EtherChannel, comparing and contrasting these two pivotal technologies. We'll explore their configurations, use cases, and how they fit into the broader landscape of network design.
Whether you're an IT professional looking to sharpen your skills or a student embarking on your networking journey, understanding these technologies is crucial.
Beyond theoretical knowledge, practical application plays a fundamental role in mastering networking concepts.
Understanding Port Channel and EtherChannel
In the realm of network design, two concepts often come up: Port Channel and EtherChannel. Though they're closely related, understanding their differences is crucial for anyone involved in network management or configuration.
What is Port Channel?
Port Channel refers to the virtual interface created in Cisco IOS platforms to represent a group of physical ports combined into a single logical link. This technique is a form of link aggregation, which essentially means taking multiple network connections and treating them as one. This has a few big benefits:
- Increases the total bandwidth available between switches or servers by combining the bandwidth of individual links.
- Provides redundancy so that if one physical link fails, the others can continue to carry the network traffic without interruption.
- Simplifies network configuration and management by allowing you to configure multiple ports as a single entity.
What is EtherChannel?
EtherChannel, on the other hand, is the technology behind the curtain. It's what makes the magic of combining several physical links into one logical one possible. EtherChannel can be thought of as the engine under the hood of Port Channel, with its own set of protocols like LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol) and PAgP (Port Aggregation Protocol) to manage the aggregation of links efficiently. It stands out for its ability to:
- Provide load balancing across the aggregated links, which optimizes the distribution of traffic for better performance.
- Offer a way to increase bandwidth without needing to upgrade to faster, more expensive single links.
- Ensure network redundancy, enhancing reliability and uptime by automatically redistribiting traffic if a link in the bundle fails.
Both Port Channel and EtherChannel are vital in creating a network that's not only faster but also more reliable and easier to manage. They ensure that networks can handle large volumes of traffic smoothly and continue operating even when individual links encounter problems.
By using these technologies, network administrators can ensure that their networks are equipped to handle the demands of modern internet traffic, whether it's in a small business or a large data center. Moreover, understanding and being able to implement Port Channel and EtherChannel is crucial for any networking professional, which is thoroughly covered in our Cisco CCNA course. This course not only dives deep into these concepts but also provides hands-on experiences to apply what you've learned in real-world scenarios.
Comparative Analysis: Port Channel vs EtherChannel
When navigating the complexities of network configurations, it’s crucial to understand not just what Port Channel and EtherChannel are, but also how they compare and when to use each. This understanding ensures that networks are not only robust and efficient but also tailored to the specific needs of the organization.
Terminology and Technology
At the core, the difference between Port Channel and EtherChannel lies in terminology and technology. Port Channel refers to the virtual interface seen in Cisco's IOS platform, essentially the name given to the logical link created by aggregating physical links. On the other hand, EtherChannel is the underlying technology that allows multiple physical links to be treated as a single logical connection. It's like comparing an engine (EtherChannel) to the car’s model name (Port Channel).
Configurations and Use Cases
Configurations of both technologies play a significant role in their application. While the configuration process itself is similar—aggregating multiple links to enhance bandwidth and provide redundancy—the protocols used can differ. EtherChannel supports LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol) and PAgP (Port Aggregation Protocol), providing flexibility depending on the devices being connected and the network requirements.
The use cases for both are broadly the same, aiming to increase bandwidth and provide network redundancy. However, the choice between using LACP or PAgP within EtherChannel might depend on whether you're integrating with non-Cisco hardware or require specific Cisco features, affecting how one might choose to implement these technologies in various scenarios.
Advantages and Limitations
Both Port Channel and EtherChannel offer significant advantages, including increased bandwidth and fault tolerance. By aggregating links, they ensure that the failure of a single physical link does not result in downtime, critical for maintaining 24/7 network availability. Moreover, they both support load balancing, which optimizes network performance by evenly distributing traffic across all available links.
However, there are limitations to consider. For instance, all physical ports in an EtherChannel must reside on the same switch, except in specific configurations like Cisco's Virtual Switching System (VSS) or Nexus vPC, which allow for more flexible deployment options. Understanding these limitations is key to designing a network that meets specific operational requirements without unexpected constraints.
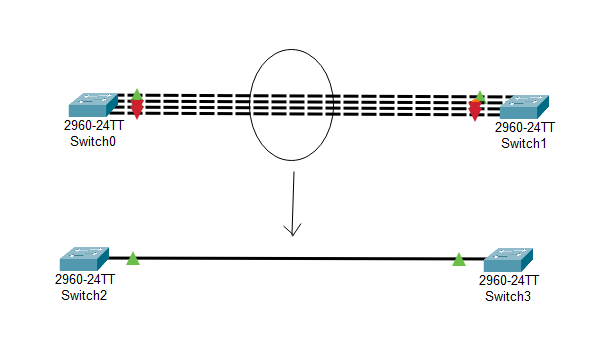
Choosing the Right Configuration for Your Network
Deciding between Port Channel and EtherChannel for your network isn’t just about technical specifications; it’s about matching the right technology with your network’s specific needs. Here’s how to make that choice clearer and ensure your network is as efficient, robust, and resilient as possible.
Consider Your Network Environment
The first step in making the right choice is to assess your network environment. Are you working within a purely Cisco ecosystem, or is your network a mix of different vendors? EtherChannel's support for LACP, an IEEE standard, makes it a versatile choice for multi-vendor environments, ensuring compatibility across devices from different manufacturers.
Evaluate Your Network Requirements
Understanding your network’s bandwidth requirements and redundancy needs is crucial. If your primary goal is to increase bandwidth by aggregating links, both Port Channel and EtherChannel can meet this need. However, if you're also looking for load balancing and fault tolerance with an easy configuration, you might lean towards EtherChannel for its automatic negotiation capabilities via LACP or PAgP.
Future-Proofing Your Network
Considering the future scalability of your network is vital. As your network grows, the ability to easily add physical links to an existing aggregation without disrupting traffic can be a deciding factor. EtherChannel's dynamic negotiation with protocols like LACP supports this scalability, allowing for seamless network expansions.
Practical Skills and Training
For those responsible for designing, configuring, and managing networks, having hands-on experience is invaluable. This is where practical training, like our Cisco CCNA 200-301 course, becomes essential. This course not only covers the theoretical aspects of Port Channel and EtherChannel but also provides practical exercises to apply these concepts in real-world settings, ensuring you have the skills needed to make informed decisions about your network configuration.
Choosing between Port Channel and EtherChannel involves a careful evaluation of your network's current and future needs, the environment in which it operates, and the technical requirements it must fulfill. By considering these factors and leveraging educational resources like the CCNA 200-301 course, you can ensure that your network is not only configured for optimal performance today but is also ready to meet the challenges of tomorrow.
Summary
In wrapping up our exploration of Port Channel and EtherChannel, it's clear that both technologies play crucial roles in enhancing network efficiency, reliability, and performance. By aggregating multiple physical links into a single logical connection, they not only increase bandwidth but also ensure redundancy and fault tolerance, essential aspects for any network's resilience.
Port Channel serves as the virtual interface, a concept within Cisco IOS platforms that simplifies the management and configuration of aggregated links.
EtherChannel, on the other hand, is the technology itself, equipped with protocols like LACP and PAgP to efficiently manage the aggregation process, offering flexibility across various network environments.
Understanding when and how to use these technologies is key for network professionals aiming to optimize their network infrastructures.
Whether it's choosing between LACP or PAgP based on hardware compatibility or understanding the limitations of link aggregation, making informed decisions is critical.
For those eager to dive deeper and master these technologies, our Cisco CCNA course offers an in-depth look at not just Port Channel and EtherChannel but a wide array of networking concepts. It's an invaluable resource for anyone looking to enhance their networking skills with both theoretical knowledge and practical, hands-on experience.


