Loop Guard is an essential feature in network environments, designed to prevent loops by providing additional protection to the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP). However, despite its critical role, various issues can arise that may compromise network stability and performance. Understanding how to efficiently tackle these common problems is vital for maintaining a robust network infrastructure.
Understanding Loop Guard Functionality
Before diving into troubleshooting, it's important to grasp how Loop Guard works. Loop Guard is used in network environments to prevent alternate or root ports from becoming designated ports due to unidirectional link failures. It's a proactive feature that enhances the STP stability by detecting failures that can lead to switching loops.
When Loop Guard is enabled, it monitors the receipt of Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs). If the BPDUs are not received on a non-designated port and it's supposed to, Loop Guard puts that port into a loop-inconsistent state, thus preventing potential loops. The efficiency of Loop Guard hinges on its proper configuration and operation in synergy with the existing network architecture.
Identifying Common Loop Guard Issues
Some of the most common issues encountered with Loop Guard include incorrect configurations, physical layer issues, and software bugs. Incorrect configurations might arise from setting Loop Guard on the wrong ports or misunderstanding its interaction with other STP enhancements like Root Guard or BPDU Guard. Physical issues often relate to faulty cabling or port failures, which can prevent BPDU transmission, erroneally triggering the Loop Guard. Software-related issues might stem from firmware bugs affecting the reliability of BPDU handling.
Incorrect Configuration
One prevalent issue with Loop Guard is incorrect configuration. This error typically occurs when Loop Guard is configured globally without considerations for specific network design essentials. To avoid such misconfigurations, understanding the network layout and how different STP enhancers interact is crucial. For deeper insights into effective Layer 2 network designs which cater to proper use of STP enhancements including Loop Guard, check out our specialized course Layer 2 Network Design.
Misconfiguration can lead to inadvertent blocking of ports or the entire VLAN, causing significant downtime and productivity loss. It's vital to periodically review and audit the network's STP and Loop Guard configurations to align with the network's operational requirements and best practices.
Another significant aspect is keeping the network's firmware updated. Outdated firmware can have unaddressed bugs that affect Loop Guard's performance. Regular updates ensure compatibility and enhance the security and stability of network operations.
In the next sections, we will explore troubleshooting steps and how to resolve physical and software issues related to Loop Guard to ensure a smooth and stable network environment.
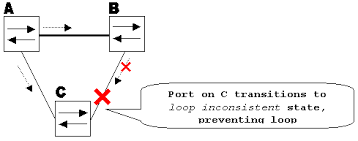
Troubleshooting Steps for Resolving Loop Guard Issues
Effectively troubleshooting Loop Guard issues requires a systematic approach. Whether dealing with configuration mistakes, physical connectivity problems, or software glitches, the following steps can help identify and resolve these issues efficiently.
Step-by-Step Troubleshooting Process
Begin with verifying the root cause of the problem. This process starts with basic diagnostics and leads up to more complex testing and configurations adjustments where necessary.
Verify Network Configuration
The first step in any troubleshooting scenario is to verify the existing configurations. Revisiting the Loop Guard settings on each relevant switch ensures that it's enabled only on appropriate ports. Incorrect application could lead to unintended network behaviors. Utilize configuration commands like show spanning-tree summary and show spanning-tree inconsistentports to gather detailed information about current STP and Loop Guard states, and identify any inconsistencies.
Check Physical Connections
A fundamental check often overlooked involves physical connections. Inspect all cables and ports involved in the Loop Guard configuration for signs of damage or disconnection. Faulty wiring can disrupt BPDU transmissions, causing Loop Guard to react by putting ports into inconsistent states. Replace any defective hardware, and ensure all connections are secure and compliant with network standards.
Examine System Logs and Alerts
Reviewing system logs provides insights into events that preceded the issue. Look for any alerts or messages related specifically to Loop Guard or spanning-tree operations. Log data can help pinpoint when the problem began and what changes might have caused it. Common alerts might involve unexpected changes in port status or lost BPDU messages, which are critical clues for resolving Loop Guard problems.
Software Update and Testing
If the issue still persists after performing hardware and configuration checks, consider a software perspective. Update the network devices' firmware to the latest version to mitigate any known bugs affecting Loop Guard's functionality. Post-update, run a series of stress tests and monitor the network stability to ensure that the issue is resolved. Employ commands like debug spanning-tree events to gain deeper insights into STP processes and Loop Guard's operational impacts during these tests.
By following these systematic troubleshooting steps, most issues related to Loop Guard can be efficiently diagnosed and remediated. Continuing to the final sections, we will conclude with preventive measures and best practices to avoid future Loop Guard issues.
Preventive Measures and Best Practices for Loop Guard
Ensuring that Loop Guard issues are minimized in the future not only involves resolving current problems but also adopting a proactive approach to network design and regular maintenance. Below are some preventive strategies and best practices that can strengthen your network against potential Loop Guard-related disruptions.
Implement Regular Monitoring and Audits
Maintaining network health is crucial for preventing issues associated with Loop Guard. Implement regular monitoring of your network's performance and configuration through automated tools and manual audits. Regular checks help in catching misconfigurations or potential problems before they escalate into major issues, ensuring Loop Guard functionality is optimal.
Systematic Configuration Management
Develop a systematic approach to configuration management. This involves documenting all changes made to the network, particularly changes that affect Loop Guard and STP settings. Using configuration management databases (CMDBs) can help in tracking historical configurations and restoring them when needed. Ensuring that all team members follow a standard protocol for making and documenting changes reduces errors and improves reaction times during troubleshooting.
Create a Robust Network Design
A robust network design includes considering how Loop Guard and other STP features will interact. Design network redundancies carefully to avoid unnecessary Loop Guard activations. Engage in thorough planning sessions and leverage detailed network diagrams to understand and manage how data flows and how protections like Loop Guard will affect the network under different scenarios.
Training and Knowledge Sharing
Continuous education on network security and stability for IT staff is critical. Ensure that all team members are updated with the latest network management strategies, STP optimizations, and best practices for Loop Guard configuration. Conducting regular training sessions and sharing knowledge resources can greatly enhance the team's ability to prevent and quickly resolve issues related to Loop Guard.
In conclusion, although Loop Guard is a powerful feature for maintaining network stability, it requires careful configuration, regular maintenance, and an aware team to function effectively. By adopting the preventive measures and best practices discussed, your team can enhance network reliability and mitigate the risks associated with network loops and other related issues.


